Authentication
Karate Tools supports the following authentication mechanisms:
- 🔐
basic -
see Basic Authentication.
- 🔐
jwt -
see JWT Authentication.
Karate Auth - Default Settings
The environment Authentication mode and default settings must be defined per environment.
-
defaultAuthMode: basic … -
defaultUsername: default username. -
credentials: pairs ofusername: password.-
For example:
-
pair
<username: password>credentials: # username: password username100: username100p -
pair
<username: system property>credentials: # username: password usernamedes: '#(karate.properties["value-injected-as-system-property"])'
-
-
| The default values for each supported authentication type are defined in the corresponding section. |
Karate Auth - Overwrite at Request Level
Each of the auth default settings can be overwritten at request level using the corresponding auth.xxx field.
-
auth.authMode -
auth.username -
auth.password
For example, for authentication and authorization tests at test data level:
-
test-data\<operation>_<returncode>.yml
auth: authMode: 'basic' username: 'usernameA' password: 'passwordA'auth: authMode: 'jwt' username: 'usernameA'
The specific values that can be overwritten (auth.XXX) for each supported authentication type are defined in the corresponding section.
|
Karate Auth - Error Management
When Karate Tools Authentication fails it can be identified through the karate logs and the karate reports.
For example:
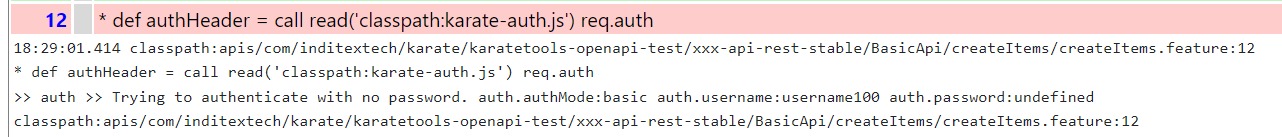
-
invalid authMode:>> auth >> Trying to authenticate with no authMode or invalid authMode. auth.authMode:BASIC -
no username:>> auth >> Trying to authenticate with no username. auth.authMode:basic auth.username:null -
no password:>> auth >> Trying to authenticate with no password. auth.authMode:basic auth.username:username100 auth.password:undefined
| The specific error messages for each supported authentication type are defined in the corresponding section. |